Rafel malware is a very dangerous infection that targets Android devices. It’s a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) type of infection, which allows its operators remote control over the infected device. If it successfully infects a device and gets the necessary permissions, it could steal sensitive data, lock it, and encrypt data.
Remote Access Trojans like Refal are considered to be one of the most dangerous infections. This particular RAT infection targets Android devices worldwide, particularly in the USA, India, China, and Indonesia. Several high-profile organizations and entities have been targeted by attackers operating this malware.
Refal can be modified to suit the needs of whoever is controlling it. Several cybercriminal groups are known to use this trojan. There are several ways the malware can get into devices, and this will be discussed in more detail below. Once it enters the device, it starts requesting permissions. If granted, the malware first collects device data, including device model, hardware details, battery information, root status, geolocation data, language settings, mobile operator, installed apps, etc.
The malware is quite stealthy and can avoid detection by imitating legitimate apps. It can allow itself to start automatically when the system boots, bypass being forced to sleep to maintain the battery, and operate in the background after the app is closed.
The trojan also misuses the Android Accessibility Services, which is a feature to help users with disabilities use their devices more conveniently. The malware uses this feature to read screens, interact with the keyboard, etc. The malware can also steal and delete files, as well as wipe the data on an SD memory card. It can also steal contact lists and call logs, read and send SMS messages, make phone calls, read notifications, and obtain multi-factor authentication codes. It can also also encrypt data on the device, as well as lock it.
Overall, the Rafel malware is a very serious infection that can result in stolen and permanently lost data, identity theft, financial loss, privacy issues, etc.
How does Rafel malware (Android) enter the device?
The Rafel malware is distributed in quite a few different ways. First of all, Rafel malware may be disguised as legitimate apps like Instagram, WhatsApp, anti-virus programs, tools, etc., and promoted on questionable download websites.
It could also be spread using phishing and social engineering attacks. This is likely the method used when malicious actors target someone specific. If they have access to personal information, they can make their social engineering attacks very convincing. However, such sophisticated attacks are usually reserved for high-profile targets.
Like with all malware, it’s possible to infect a device with Rafel RAT when downloading cracks and pirated content. Malware is very prevalent on various third-party app stores and dubious download sites as well.
One method of distribution that’s specific to the Rafel malware infection is impersonating a Telegram-based clicker game known as Hamster Kombat. The game has become very popular because it promises to hold what essentially are cryptocurrency giveaways. The game has become very popular in 2024, which is why malicious actors are impersonating it to infect devices with serious malware. This fake version of the Hamster Kombat game is being distributed through unofficial Telegram channels. When the app is downloaded, it immediately asks for alarming permissions, including to become the default SMS application.
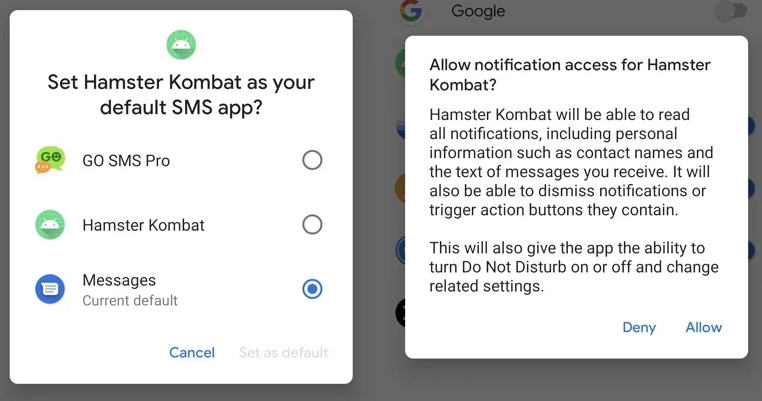 Image source: ESET WeLiveSecurity
Image source: ESET WeLiveSecurity
How to protect yourself from Android malware
- Research apps before downloading
Carefully inspecting apps before installing them onto your device should become a habit if you want to avoid malware in the future. Even when downloading an app from a legitimate source, you need to check the developer, read the reviews, inspect what permissions are requested, etc.
- Use legitimate stores/platforms to download apps
To avoid installing questionable or malicious apps, stick to official stores and download platforms. Third-party app stores not only have poor security but are also badly regulated, which allows malicious actors to upload malicious apps that stay up for a long time, infecting thousands of users before they’re taken down. While malware does occasionally sneak past Google’s security and gets uploaded onto the Google Play Store, the chances of downloading something malicious from the Play Store are significantly lower.
- Always carefully review requested permissions
When you install an app onto your device, it asks for permission to be able to operate as it should. To protect yourself from malicious apps, do not blindly click “Allow” when a permission request pops up. Always question why a particular app would need the permissions it asks for. For example, if you download a game and it requests permission to read your messages, make calls, etc., that should be an immediate red flag.
- Keep your device up-to-date
Vulnerabilities are discovered all the time by developers and updates are released to patch them up. If you skip out on the updates, your device becomes vulnerable to cyberattacks.
- Do not click on unknown links or open unsolicited email attachments
Be very careful with unsolicited links received via SMS, email, messaging apps, etc. Never click on unknown links, and keep in mind that government agencies (e.g. law enforcement, tax agencies), banks, and other institutions do not send SMS messages with links. You should also never open unsolicited email attachments without double-checking them first.
Site Disclaimer
2-remove-virus.com is not sponsored, owned, affiliated, or linked to malware developers or distributors that are referenced in this article. The article does not promote or endorse any type of malware. We aim at providing useful information that will help computer users to detect and eliminate the unwanted malicious programs from their computers. This can be done manually by following the instructions presented in the article or automatically by implementing the suggested anti-malware tools.
The article is only meant to be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions given in the article, you agree to be contracted by the disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the artcile will present you with a solution that removes the malign threats completely. Malware changes constantly, which is why, in some cases, it may be difficult to clean the computer fully by using only the manual removal instructions.