Insom ransomware is file-encrypting malware that belongs to the Makop ransomware family. If it successfully infects a computer, it encrypts all personal files and demands payment for their decryption. This ransomware also threatens to post the files on a TOR website if victims do not agree to pay.
When users open an infected file, the ransomware is initiated. It immediately encrypts personal files, including photos, videos, and documents. You will not be able to open these files.
You will be able to easily recognize encrypted files because their titles will have an extension added to them. For example, a 1.txt file would become 1.txt.[unique ID].[insomrans@outlook.com].insom if encrypted. Unfortunately, until these files have been run through an Insom ransomware decryptor, you will not be able to open them.
The ransomware drops a +README-WARNING+.txt ransom note which doesn’t really explain much. It just mentions that your data has been stolen and will be published on a TOR website unless you contact the malware operators. It also does not mention the price you would be expected to pay but whatever it is, we do not recommend paying. Malware operators are cybercriminals who do not care about helping victims. Nothing is stopping cyber criminals from just taking your money, not sending anything in return, and still posting the stolen data. It has happened many times in the past. Furthermore, the ransom money will go toward future criminal activities.
If you do have a backup, remove Insom ransomware from your computer before you can access it, and make sure to use a good anti-malware program because it’s a complex infection. If you don’t have a backup, your only option is to wait for a free Insom ransomware decryptor. A free Insom ransomware decryptor is not guaranteed but if does get released, it will be downloadable from NoMoreRansom.
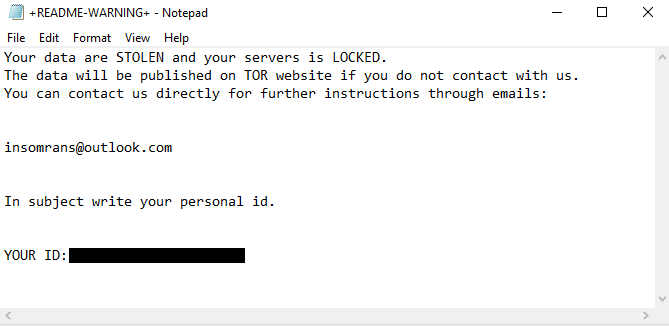
Below is the full Insom ransomware ransom note:
Your data are STOLEN and your servers is LOCKED.
The data will be published on TOR website if you do not contact with us.
You can contact us directly for further instructions through emails:insomrans@outlook.com
In subject write your personal id.
YOUR ID:
How does ransomware enter computers?
Users who have poor browsing habits are much more likely to infect their computers with malware compared to users who do not engage in risky online behavior. Developing better online habits is strongly recommended to avoid future malware infections.
Learning to recognize malicious emails is important, particularly if your email address has been leaked because you are bound to receive a malicious email sooner or later. Fortunately, unless you are targeted specifically, malicious emails are very generic, which makes them easy to recognize. For one, they’re often full of grammar and spelling mistakes. Senders pretend to be from legitimate companies, so the mistakes are very jarring.
Generic words like User, Member, Customer, etc., being used to address you can be another sign that you are dealing with a malicious, or at least a spam email. When companies email customers, they always use users’ names to address them because it makes the emails seem more personal. However, malicious actors use generic words because they usually don’t have access to more personal information. For example, if you receive an unexpected order confirmation email that uses a generic greeting, be cautious because the attachment could be malicious.
Malicious emails that have specific targets are significantly more sophisticated. They do not have grammar/spelling mistakes, contain information that gives the emails more credibility, and address users by name. To avoid opening something malicious, scanning all unsolicited email attachments with anti-malware software or VirusTotal is strongly recommended.
Torrents are another way malware is distributed. It’s common for torrent sites to be poorly moderated, which allows torrents with malware to stay up for a long time. Malware can commonly be found in torrents for entertainment content, including movies, TV series, and video games. Downloading copyrighted content using torrents is not only content theft but also dangerous for the computer.
Insom ransomware removal
Do not try to remove Insom ransomware manually because you could end up causing additional damage to your device unless you know exactly what to do. Instead, use an anti-malware program. Unfortunately, removing the malware does not decrypt files. A special decryptor is necessary for that.
If you have a backup, you can start recovering your files as soon as you remove Insom ransomware from your computer. Keep in mind that if ransomware is still present on your computer when you connect your backup, backed-up files will become encrypted as well. If you do not have a backup, back up your encrypted files and occasionally check NoMoreRansom for a free Insom ransomware decryptor.
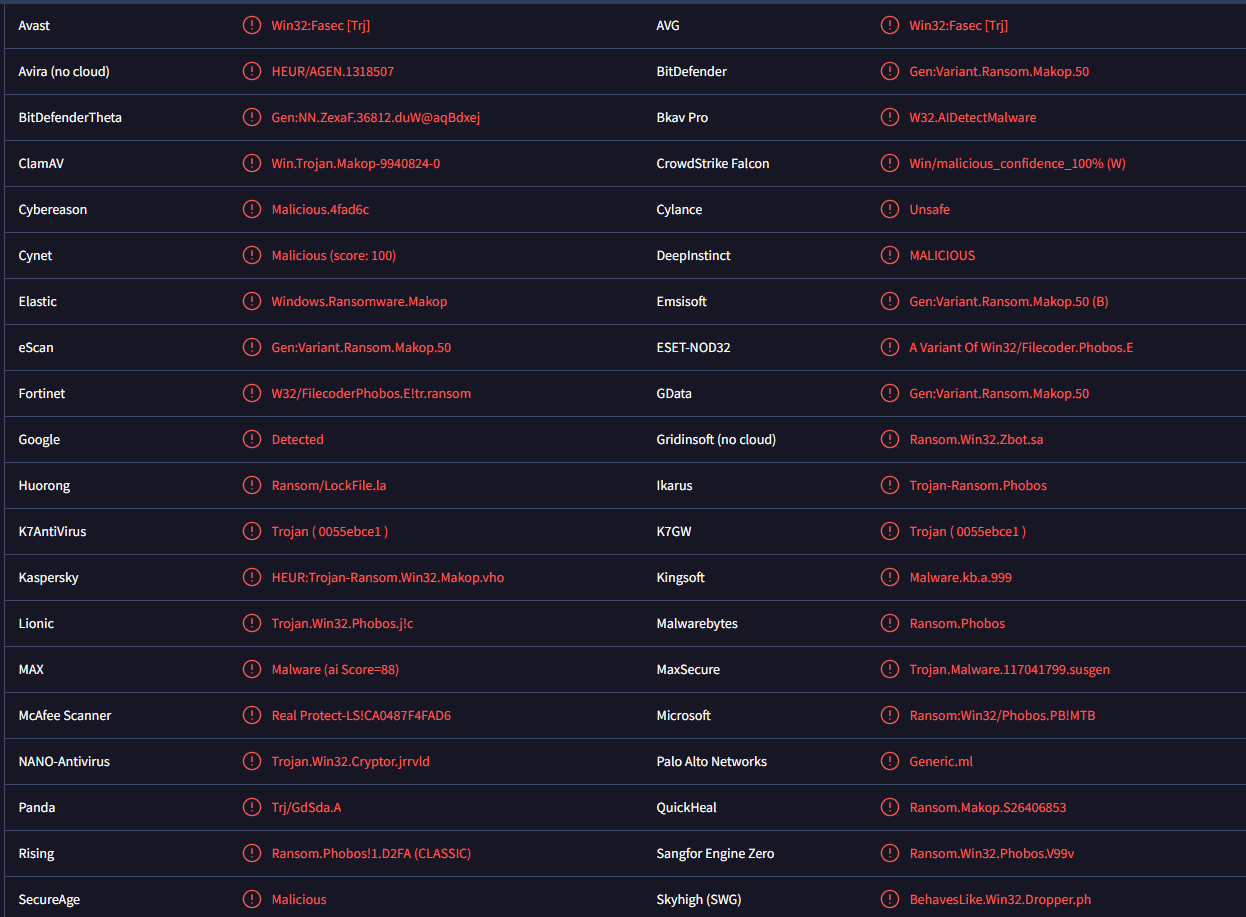
Insom ransomware is detected as:
- Win32:Fasec [Trj] by AVG/Avast
- Gen:Variant.Ransom.Makop.50 by BitDefender
- A Variant Of Win32/Filecoder.Phobos.E by ESET
- HEUR:Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Makop.vho by Kaspersky
- Ransom.Phobos by Malwarebytes
Site Disclaimer
2-remove-virus.com is not sponsored, owned, affiliated, or linked to malware developers or distributors that are referenced in this article. The article does not promote or endorse any type of malware. We aim at providing useful information that will help computer users to detect and eliminate the unwanted malicious programs from their computers. This can be done manually by following the instructions presented in the article or automatically by implementing the suggested anti-malware tools.
The article is only meant to be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions given in the article, you agree to be contracted by the disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the artcile will present you with a solution that removes the malign threats completely. Malware changes constantly, which is why, in some cases, it may be difficult to clean the computer fully by using only the manual removal instructions.